Reviewing SCERT Kerala Syllabus 7th Standard Basic Science Notes Pdf and Class 7 Basic Science Chapter 9 Question Answer Notes Solutions Pdf Hurt not the Environment can uncover gaps in understanding.
Hurt not the Environment Class 7 Questions and Answers Notes
Class 7 Basic Science Chapter 9 Hurt not the Environment Question Answer Pdf
Basic Science Class 7 Chapter 9 Question Answer Kerala Syllabus
Let Us Assess
Question 1.
Observe the diagrams given below. Find out how the air gets polluted in each situation and complete the table.

Answer:
| Situation | Ways of Air Pollution | Consequences |
| Construction Site | Dust particles from digging, moving, and sifting materials | Respiratory problems, eye irritation, damage to lungs and heart |
| Demolition Site | Dust, debris, and other particulate matter from the demolition process. | Respiratory problems, eye irritation,damage to lungs and heart. |
| Industrial Area | Smoke and exhaust gases from factory chimneys | Respiratory problems, acid rain, global warming, damage to plants and ecosystems |
| Traffic Congestion | Vehicle exhaust gases from burning fossil fuels | Respiratory problems, heart disease,acid rain, global warming, smog |
Question 2.
Prepare posters calling for the prevention of environmental pollution.
Answer:

Question 3.
Identify the correct statements regarding plastic waste management from those given below:
a) Thin plastic products should be burnt.
b) Plastic products should be recycled as much as possible.
c) Plastic products should be reused as much as possible.
d) Use of plastic products should be minimised.
Answer:
b) Plastic products should be recycled as much as possible.
c) Plastic products should be reused as much as possible.
d) Use of plastic products should be minimised.
![]()
Question 4.
Which method of purification can be adopted to separate freshwater from seawater?
a) Sifting
b) Chlorination
c) Distillation
d) Sedimentation
Answer:
c) Distillation
Class 7 Basic Science Chapter 9 Extended Activities Answers
Question 1.
Take moist soil in a pot. Bury a fruit peel and a plastic wrap in the potting soil simultaneously. Observe them after two weeks. Prepare a note based on your findings.
Answer:
The fruit peel decomposes naturally in soil, while plastic wrap remains intact or shows minimal signs of decomposition. The experiment demonstrates that organic materials like fruit peels decompose naturally, while plastic is not biodegradable.
Question 2.
Prepare a speech on ‘Vehicles and Air Pollution.’
Answer:
Good moming/aftemoon, everyone.
Today, I want to talk about air pollution caused by vehicles. As our cities grow, more people rely on cars, bikes, and buses, which has worsened the air we breathe. Vehicles that run on petrol and diesel are big contributors to air pollution. When these fuels bum, they release harmful substances into the air.
One of these is particulate matter, which can get deep into our lungs and cause breathing problems. Nitrogen oxides lead to smog and acid rain, while carbon monoxide is a poisonous gas that can be very dangerous. Carbon dioxide, another gas released, is a greenhouse gas that adds to global warming.
This problem is especially bad in cities because of the large number of vehicles and traffic jams. People living in cities often suffer from health problems like breathing issues and heart diseases due to air pollution. Switching to electric vehicles can help reduce this pollution.
Air pollution from vehicles is a serious issue, and we must act now. By using cleaner fuels and reducing our use of fossil fuels, we can improve the air we breathe and make the world healthier for future generations. Thank you.
Question 3.
Prepare a short note based on an activity carried out at your home on a project implemented by the Local Self Government for waste management. Present it before the class.
Answer:
Our local self-government initiated a waste management project to address environmental concerns. During the clean-up, we found significant plastic waste, emphasising the need for recycling. The project raised awareness about waste management. We can contribute by reducing single-use plastic consumption, segregating waste, participating in recycling initiatives, and educating others.
![]()
Question 4.
Create and display a logo in connection with making your school a Zero Waste Green School.
Answer:
Class 7 Basic Science Chapter 9 Intext Question and Answers
Question 1.
Have you seen such sights? List such situations you have observed and the problems caused by them.
Answer:
| Situations | Problems |
| Plastic being burnt | Air gets polluted due to smoke. |
| Air Pollution from vehicular emissions | Vehicles, especially older or poorly maintained ones, release harmful gases like carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides. |
| Improper industrial waste disposal | Factories discharging untreated waste into rivers and lakes. |
Question 2.
Which are the substances produced when solid waste, including plastic, is burnt?
Answer:
Carbon monoxide, Sulphur dioxide, Nitrogen dioxide, Particulate matter, dioxins etc.
Question 3.
Won’t there be unburnt remains while burning plastic and other materials? What will happen to these unburnt remains when it rains? What are the consequences of such situations? Analyse the illustration given below and write your findings in the Science Diary.
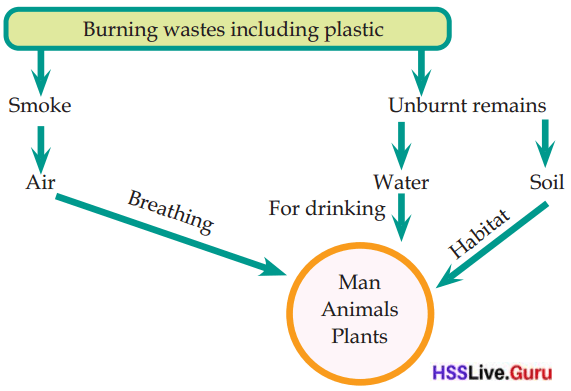
Answer:
The burning of plastic releases harmful smoke into the atmosphere. The smoke contains toxic chemicals like dioxins and particulate matter, which pollute the air. Humans, animals, and plants are exposed to this polluted air, leading to breathing issues and long-term respiratory diseases. When plastic is burned and leaving behind unbumt remains. These remains can mix with water or seep into the soil. This will result in contamination of drinking water for humans, animals, and plants.
![]()
Question 4.
What chemical substances are present in the smoke produced when plastic is burnt? How do they affect our health?
Answer:
| Chemical substances are produced when wastes, including plastic, are burnt. | Health issues affecting humans |
| Carbon monoxide | Causes cardiovascular and respiratory diseases. |
| Sulphur dioxide | Causes respiratory diseases. |
| Nitrogen dioxide | Inhalation causes itching in the throat and eyes, allergies, asthma and lung cancer. |
| Particulate matter | Increases the risk of cancer and causes thyroid-related problems and respiratory diseases. |
| Dioxins | Even when a small amount reaches the body, problems like headache, fatigue, blurred vision, and memory loss occur. Inhalation of large quantities of carbon monoxide leads to death. |
Question 5.
Which are the chemical substances released while burning waste materials including plastic?
What are the health issues caused as a result of this? Write them in the Science Diary.
Answer:
Burning waste materials, including plastic, releases harmful chemicals like carbon monoxide, sulphur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, dioxins, and particulate matter into the air. These chemicals can cause serious health problems such as breathing issues, heart diseases, and even cancer.
Question 6.
Does air pollution cause changes in the components of air?
Answer:
Yes, air pollution causes changes in the components of air by introducing harmful substances, such as chemicals, particulates, and biological materials, into the atmosphere. These pollutants can alter the natural composition of air.
Question 7.
Which are the elements found naturally in the air? Observe the given pie diagram and tabulate their quantities.
a. What are the components present in atmospheric air?
b. Which is the most abundant component?
c. What is the quantity of oxygen in the air?
Answer:
The elements found naturally in the air include Oxygen, Carbon dioxide, Nitrogen and others.
| Elements | Composition |
| Oxygen | 21% |
| Nitrogen | 78% |
| Carbon dioxide | 0.04% |
| Others | 0.96% |
a. Nitrogen, Oxygen, Carbon dioxide and others.
b. Nitrogen
c. 21%
When the atmospheric air is mixed with chemical substances, the quantity of natural constituents in the air changes.
Question 8.
Which types of stoves are used for cooking?
Answer:
The different types of stoves that are used for cooking include Firewood stoves, Kerosene stoves, Gas stoves, electric stoves, etc.
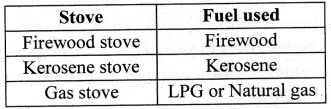
When fuels like wood, kerosene and cooking gas are burnt, various chemical substances are released. The chemical substances released are mainly carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, particulate matter, etc.
Question 9.
What measures should be taken to control air pollution in the kitchen due to the burning of cooking fuels? Discuss with friends and write in the Science Diary.
Answer:
- Construction of chimneys
- Proper ventilation
- Regular maintenance of stoves
- Usage of cleaner fuels such as LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas), natural gas, or electric stoves instead of firewood stoves.
Question 10.
As in the kitchen, don’t we use different types of fuels in our vehicles? Which are the fuels commonly used in vehicles? Write them in the Science Diary.
Answer:
Petrol, Diesel, CNG, and Electricity.
Question 11.
The change in the number of automobiles in Kerala since 2013 is shown in the bar diagram below.
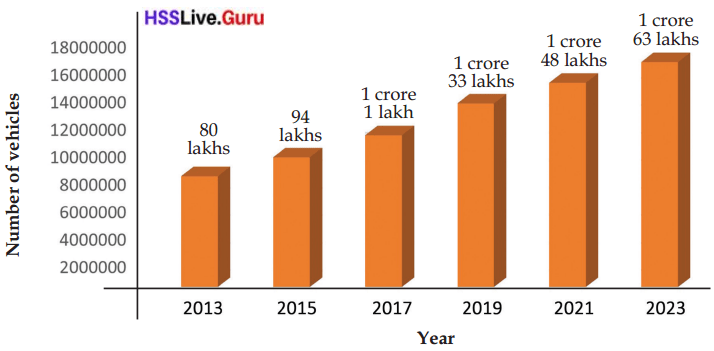
a. What was the approximate number of vehicles in 2013?
b. What was the number of vehicles in 2023?
c. What is the change in the number of vehicles from 2013 to 2023?
Answer:
a. 80 lakhs (8 million).
b. 1 crore, 63 lakhs (16.3 million).
c. The change in the number of vehicles from 2013 to 2023 is 83 lakhs.
Question 12.
How does the increase in petrolídiesel vehicles affect the air? Haven’t you seen instances where only one person is travelling in one vehicle, which can accommodate more passengers? Shouldn’t this be avoided as much as possible?
Answer:
Vehicles that run on petrol and diesel release harmful gases like carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides, which pollute the air.
Travelling alone in a car uses more fuel and adds to traffic jams. To reduce pollution, it’s better to use public transport like buses and trains instead of driving alone.
Question 13.
How does the use of vehicles like bicycles benefit the environment? Present your findings in the class.
Answer:
Bicycles are great because they don’t use fuel, so they don’t release carbon dioxide or other harmful gases that harm the air and climate. They take up less space, helping reduce traffic and pollution. Bicycles run on human energy, saving fuel, and are quiet, lowering noise in cities.
Question 14.
How does smoke testing help to reduce air pollution? Discuss in your class. Visit a Vehicle Pollution Testing Centre arid find out the activities going on there.
Answer:
Smoke testing helps identify if a vehicle’s emissions contain more harmful chemicals due to engine problems, age, or bad fuel, helping to reduce air pollution. During vehicle inspection, technicians check the exhaust and engine to ensure they are working properly. Then, the vehicle is connected to an emission testing machine to measure the pollution level. If the vehicle passes, a Pollution Under Control (PUC) certificate is given. If it fails, the owner is advised to make repairs and return for another test.
![]()
Question 15.
What are your comments on the use of vehicles regarding air pollution control? Write them in your Science Diary and present them in the class.
Answer:
Electric vehicles are a great way to reduce air pollution. Fewer vehicles on the road mean less pollution, so using public transport or carpooling helps. For short trips, walking or biking not only reduces pollution but also improves health. Keeping vehicles well-maintained and using cleaner fusls can also help cut down air pollution.
Question 16.
We have discussed air pollution caused by burning fuels and other substances. Apart from this, what are the other ways by which air gets polluted?
Answer:
Factories and industrial plants release harmful gases such as sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, which can cause smog and acid rain. Chemical fertilisers and pesticides also add pollutants like ammonia and methane to the air. Natural events like volcanic eruptions, wildfires, and dust storms are other sources of air pollution.
Question 17.
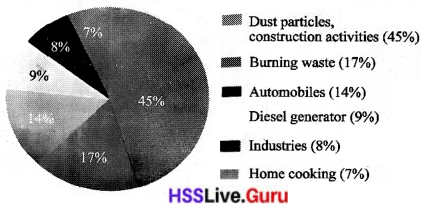
Analyse the Pie diagram given below and find out how air pollution occurs in our country. How does air pollution occur? Based on the Pie diagram, prepare a note on your findings and present it in the class.

Answer:
The biggest source of air pollution is dust from construction activities. Automobiles contribute 14% to air pollution, while diesel generators add 9%, industries contribute 8%, and home cooking adds 7%.
From the pie chart, it’s clear that construction, burning waste, and vehicle emissions are the main causes of air pollution in India. When vehicles burn fossil fuels, they produce harmful gases like carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides. Factories also release pollutants such as sulphur dioxide and volatile organic compounds into the air.
Question 18.
Conduct a seminar in your class on air pollution, its causes and remedies.
Answer:
The main causes of air pollution include industrial emissions, vehicle emissions, and construction dust. Factories release harmful gases like sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. Vehicles burning fossil fuels produce carbon monoxide. Cooking, heating, and burning waste add to pollution. Natural events like volcanic eruptions and forest fires also contribute, while deforestation reduces forests’ ability to absorb carbon dioxide.
We can reduce air pollution by using public transport, carpooling, and switching to electric vehicles. Saving energy by turning off appliances when not in use. Planting more trees improves air quality as they absorb carbon dioxide. Proper waste management and Promoting renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydropower is also needed.
Question 19.
You know that two-thirds of the Earth is water. What are the different forms of water found on the Earth?
Answer:
- Ice caps, glaciers etc.
- Water vapour, Fog
- Snow, Icebergs
- Freshwater, Saltwater, Wetlands, Rain and Dew
Question 20.
How do water bodies get polluted?
Answer:
- Disposal of plastic wastes
- Spillage of chemical substances
- Factories release harmful chemicals and toxic waste directly into rivers and lakes.
- Thermal pollution happens when factories release hot water into rivers or lakes.
- Sewage from homes, including human waste.
Question 21.
A water body polluted by algae. What is the reason for this condition of the water body?
Answer:
Eutrophication.
Question 22.
By analysing the pictures given below and observing your surroundings, find out the situations that cause water pollution and write them in the Science Diary.
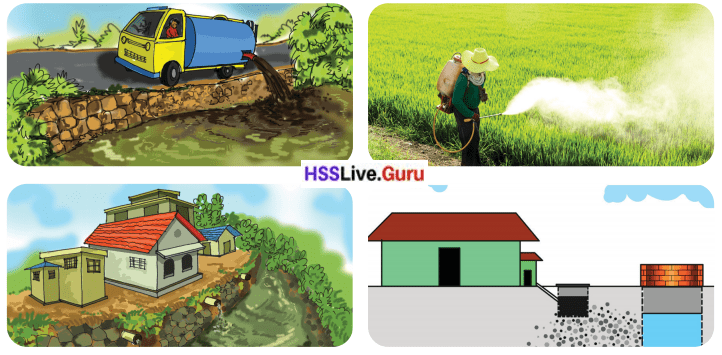
Answer:
- Excessive use of chemical pesticides.
- Discharge of wastewater into drainages.
- Dumping of slaughterhouse waste in land and water bodies.
- Discharge of waste from industries into water bodies.
- Untreated sewage discharge into water bodies.
- People are throwing garbage, plastic, and household waste directly into water bodies.
Question 23.
You have listed the situations related to water pollution. Discuss its consequences and write them iff your Science Diary.
Answer:
Polluted water contains harmful germs like bacteria, viruses, and parasites that can cause diseases such as cholera, typhoid, dysentery, and hepatitis. Toxic chemicals, sewage, and plastic waste harm fish and other aquatic animals. Pollutants like microplastics and heavy metals can build up in their bodies. Chemicals from landfills, factories, and farms can also seep into the ground, contaminating groundwater.
![]()
Question 24.
What measures can we adopt to make water sources free from pollution? Discuss.
Answer:
Reducing waste, recycling materials, and reusing products can help minimise the amount of waste. Encourage the use of organic fertilisers and natural pest control methods.
Question 25.
What are the sources of drinking water in your school?
Answer:
Tap Water, Water Dispensers, Filtered Water Stations, Bottled Water, and Groundwater.
Question 26.
What are the qualities drinking water should have? In the following statements, put a tick against the qualities that drinking water should possess.
Clearwater
Colourless and odourless
Free from germs
Absence of hazardous chemical substances
Presence of adequate mineral salts
Salty taste
Neither acidic nor basic
Answer:
Clearwater
Colourless and odourless
Free from germs
Absence of hazardous chemical substances
Presence of adequate mineral salts
Salty taste
Neither acidic nor basic (neutral pH)
Question 27.
Collect samples of drinking water and test the following characteristics:
• Colour
• Odour
• Acidic/basic nature
• Presence of insoluble impurities
What materials are required for doing the experiment?
Answer:
Hand lens, Filter paper, Universal indicator, Transparent glass beaker or test tube, Cotton wool, pH paper (litmus paper), Funnel, Stirring rod, Distilled water.
Question 28.
How can we observe the colour and odour of water?
Answer:
To check the colour of the water, use a clear glass beaker and white paper. Pour the water into the beaker and place it in front of the white paper. If the water is clear and colourless, it’s safe to drink. If you notice any tint or cloudiness, it may contain impurities.
To check the odour of water, use a clean glass container and cotton wool. Pour the water into the container, cover it with cotton wool, and gently swirl it. Then, smell the water. Drinking water should have no smell. If it has a strange odour, it might have impurities.
Question 29.
What characteristics of water can be identified using filter paper and hand lens?
Answer:
The filter paper can be used to identify the presence of insoluble impurities present in the water. The hand lens helps you identify the size and type of impurities, such as tiny sediments, dust particles, or organic material.
Question 30.
Can’t you find out whether water is acidic or basic using a universal indicator? Check the samples of drinking water you have collected. Collect data and tabulate. Analyse the data and record the results in your Science Diary. Present them before the class.
Answer:
Yes, we can use a universal indicator to determine whether water is acidic, basic, or neutral. The universal indicator will change colour based on the pH of the water sample. Gather drinking water samples from various sources (e.g., tap water, bottled water, rainwater, well water). Add a few drops of universal indicator solution to each water sample, or dip the indicator paper in the water.
| Sample Source | Colour of Universal Indicator | pH value | Acidic/Basic/Neutral |
| Tap Water | Green | 7 | Neutral |
| Bottled Water | Greenish-blue | 7.5 | Slightly Basic |
| Well Water | Green | 7 | Neutral |
| Rain water | Yellowish-green | 6.5 | Slightly Acidic |
Question 31.
Shouldn’t the drinking water be purified if it is contaminated with impurities?
Answer:
The drinking water can be purified using different techniques like Boiling, Sifting, Sedimentation, Chlorination, and Filtration.
Question 32.
Enquire other ways to purify drinking water. Record them in Science Diary.
Answer:
Ceramic Filtration:-Water passes through porous ceramic filters, which trap bacteria and sediments. Iodine Treatment:- Iodine tablets or solutions are added to water to disinfect it. Biosand Filter:- A sand-based filtration system where water passes through layers of sand and gravel. Ion Exchange:- Effective for softening water by removing hard minerals like calcium and magnesium. It can remove some heavy metals like lead, mercury, and cadmium.
Question 33.
Which of the water purifying methods are used in your home and school? Write them in the Science Diary.
Answer:
Filtration, reverse osmosis (RO), or boiling.
Question 34.
Observe the headlines and the picture of the news given below. What are the things mentioned in this news? How do such habits of some people in our society affect the environment? Write your findings in the Science Diary and present them before the class.

Answer:
The image indicates the illegal dumping of waste. A sign indicates that dumping garbage in this area is punishable, likely by law. A reward of 2500 is promised to anyone who provides information about the people illegally dumping garbage.
Uncontrolled garbage dumping can lead to contamination of groundwater and nearby water bodies with harmful chemicals. Accumulation of waste can release foul odours and methane, a greenhouse gas, contributing to air pollution and climate change. Stagnant garbage can attract pests, rodents, and mosquitoes, leading to the spread of diseases such as malaria, cholera, and dysentery.
Question 35.
List out the different kinds of waste formed in a household?
Answer:
Fruit peel, Vegetable waste, Plastic covers, Aluminum cans, Glass bottles, Newspapers, Cardboard boxes, Old batteries, Bulbs, CFLs, Wires and cables.
![]()
Question 36.
Classify wastes into biodegradable and non-biodegradable.
Answer:
| Biodegradable | Non-Biodegradable |
|
|
Question 37.
Which type of waste cause soil pollution? Discuss.
Answer:
Plastic bags, bottles, and other plastic items take hundreds of years to decompose. Discarded electronics release harmful substances like lead, mercury, and cadmium into the soil, thereby affecting its quality and contaminating water supplies. Pesticides and Herbicides used in agriculture, if not used properly, can accumulate in the soil, poisoning the ecosystem.
Question 38.
Certain household wastes are mentioned below:
Bulbs, food wastes, CF lamps, paper, paper cups, footwear, bags, clothes, pesticide containers, paint containers, plastic bags, vegetable wastes, cardboard packing materials, plastic cups, mobile phone batteries, plastic bottles, glass bottles, empty toothpaste tube, fish and meat waste.
Classify and tabulate them in such a way that they can be deposited in the appropriate bins shown in the figure.
Answer:
| Biodegradable | Non-biodegradable | Hazardous |
| Food Wastes Paper Paper Cups Vegetable Wastes Cardboard Packing Materials fish and meat waste |
Bulbs Footwear Bags (Plastic) Clothes Plastic Bags Plastic Cups Plastic Bottles Empty Toothpaste Tube |
CF Lamps Pesticide Containers Paint Containers Mobile Phone Battery Glass Bottles |
Question 39.
What is the advantage of sorting waste at its origin itself?
Answer:
Segregated waste can be directed to proper recycling plants, ensuring plastic, metal, paper, and glass materials are reused instead of ending up in landfills. Organic waste, when separated, can be turned into compost, enriching the soil and reducing the need for chemical fertilisers.
Question 40.
What should we do after sorting the garbage? Let’s discuss.
Answer:
Biodegradable waste at home is collected for composting. Many municipalities have separate bins for organic waste. Non-biodegradable wastes like plastics, metals, and glass items are sent to recycling centres or collected by local waste management authorities. Hazardous waste like chemicals, batteries, and electronic waste should go to designated collection points or recycling centres equipped to handle such waste.
Question 41.
Observe the picture. Are you familiar with this system? Find out how it works.

Answer:
A biocomposter bin works by allowing air to flow through multiple tiers where organic waste is added. Microorganisms in the bin break down the waste with the help of oxygen and heat. Over time, the waste decomposes into compost, a nutrient-rich material used for gardening.
Question 42.
Visit a biogas plant and learn about its working. Write it in the Science Diary.
Answer:
A biogas plant works by using organic waste in a sealed container called a digester. Inside, bacteria break down the waste without oxygen (anaerobic digestion), producing biogas (mainly methane) and a by-product called digestate. The biogas is used as a renewable energy source, and the digestate can be used as fertiliser.
Question 43.
We can manage biodegradable waste generated at home and school using the above methods. Collect more details about each method.
Answer:
Vermicomposting: It is a method of composting where earthworms break down organic waste like food scraps and plant material. The worms eat the waste and produce nutrient-rich castings, which are a natural fertiliser. The process requires a moist, oxygen-rich environment and results in high- quality compost that improves soil health.
Air Contact Composting: A biocomposter bin works by allowing air to flow through multiple tiers where organic waste is added. Microorganisms in the bin break down the waste with the help of oxygen and heat. Over time, the waste decomposes into compost, a nutrient-rich material used for gardening.
Biogas Production: A biogas plant works by using organic waste in a sealed container called a digester. Inside, bacteria break down the waste without oxygen (anaerobic digestion), producing biogas (mainly methane) and a by-product called digestate. The biogas is used as a renewable energy source, and the digestate can be used as fertiliser.
![]()
Question 44.
Paper and paper products can be recycled. But can all non-biodegradable waste be disposed in the same way?
Answer:
No. Nonbiodegradable waste includes materials like plastics, metals, glass, and electronic waste (e-waste), but each type needs to be handled differently.
Question 45.
What would be the reason for banning the production and distribution of very thin plastic covers?
Answer:
Thin plastic covers are a significant source of waste often found in waterways, oceans, and landscapes.
Question 46.
What measures can be taken to reduce nonbiodegradable waste?
Answer:
Use reusable bags, bottles, and containers instead of single-use plastic items like bags, straws, and cups. Encourage plastic-free packaging for products. Switch to biodegradable or eco-friendly materials like bamboo, cloth, or metal instead of plastics.
It is the strategy adopted worldwide to reduce the amount of non-biodegradable waste. It has to become a part of our life and culture.
| R-Reduce (minimised use) | R-Reuse (Reusable) Only those with standard grades | R-Recycle (Recyclable) |
| Plastic cups | Plastic bags | Metal products |
| Plastic, thermocol plates | Plastic jars | Plastic products |
| Mineral water bottle | Plastic utensils | Aluminium cans |
Question 47.
Enquire more about the activities of Haritha Karma Sena and write them in the Science Diary. Collect information about such activities, prepare a report and present it before the class.
Answer:
Haritha Karma Sena members collect segregated waste (biodegradable and non-biodegradable) directly from households. They educate the public on the importance of sorting waste into categories like biodegradable, recyclable, and hazardous waste, encouraging sustainable waste disposal practices. Non-biodegradable waste like plastics and metals are taken to recycling facilities. Haritha Karma Sena works closely with local self-government bodies to ensure efficient waste collection and disposal.
Question 48.
We have understood the various situations in which air, water and soil are polluted and their consequences. Conduct a study to find whether such conditions exist in your locality for air, water and soil. Write your hypotheses regarding this topic in your Science Diary.
Answer:
Air Pollution Hypothesis: There are high levels of air pollution in our locality due to traffic and industrial emissions.
Water Pollution Hypothesis: The local water sources are contaminated with pollutants from nearby industries and improper waste disposal.
Soil Pollution Hypothesis: The soil in our locality is polluted due to the excessive use of fertilisers and improper waste management.
Question 49.
What observations are needed for conducting the study? What information are to be collected? Analyse the data and prepare a project report including your findings and recommendations. Present it before the class and invite guests and discuss.
Answer:
Use air quality monitors or check local air quality indices. Observe and record traffic patterns, industrial activities, and the presence of greenery. Test water from local sources (wells, rivers, or taps) for pH, turbidity, and contamination indicators (like bacteria). Observe the colour and odour of water for the identification of pollution. Collect soil samples from various locations (near schools, parks, and industrial areas). Observe the presence of garbage, chemicals, or unusual plant growth.
Question 50.
Discuss in class the steps you can take to make your school a waste-free green school.
Answer:
| Objectives | Actions to be taken |
| Garbage disposal of noon-meal |
|
| Paper waste disposal |
|
| Plastic waste disposal |
|
| Constructing Biodiversity Park |
|
Hurt not the Environment Class 7 Notes Extra Questions and Answers
Question 1.
The main factor of air pollution is ………..
Answer:
Carbon dioxide.
Question 2.
What can be done for garbage disposal?
Answer:
- Sorting garbage by type and disposing of it.
- Making biofertilisers using organic waste.
- Controlling the use of plastics and reusing them.
- Never throw away waste materials.
- Reuse that can be recycled.
- Follow the important rules and regulations connected with the protection of the environment and pronouncements.
Question 3.
What are the health issues created by the carbon monoxide from vehicle emissions?
Answer:
Even when a small amount of carbon monoxide reaches the body, problems like headache, fatigue, blurred vision, and memory loss occur. Inhalation of large quantities of carbon monoxide leads to death.
Question 4.
What are the components present in atmospheric air?
Answer:
The elements found naturally in the air include oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen and others.
Question 5.
What is air pollution, and explain the factors affecting it?
Answer:
Air pollution is caused by the mixing of smoke, toxic gases and other chemical substances in the atmospheric air. Wildfires and natural phenomena like volcanic eruptions and earthquakes also contribute to air pollution. Indiscriminate actions of human beings are the main cause of air pollution.
Question 6.
Substances, which undergo decomposition, are used to produce
Answer:
Compost
![]()
Question 7.
………….. decompose organic matter and thus improve the fertility of the soil.
Answer:
Microorganisms
Question 8.
How can we protect water sources from getting polluted? Prepare an action plan to keep the water sources in your locality pollution-free.
Answer:
- Do not allow the putting of wastewater from factories and industries into the river, pond, etc.
- Avoid washing vehicles near water sources.
- Avoid washing of cattles near water sources.
- Avoid situations in which human excreta is mixed in water.
Question 4.
What are the harmful effects that cause soil pollution?
Answer:
- The natural condition of the soil is ruined.
- Its capacity for holding water is reduced.
- The poisons in the pollutants reach plants and animals.
- Through food, these poisons reach man.
- The bad effects of radiation.
Question 5.
What do you mean by eutrophication?
Answer:
Excess growth of water plants like algae in water bodies is caused by a phenomenon known as eutrophication. This happens in water bodies where fertilisers containing nitrogen and other similar substances flow in. It is such flowing excess nutrients that cause excessive growth of aquatic plants. These aquatic plants use oxygen dissolved in water excessively. Due to this, other plants and animals in water die without getting oxygen and the ecosystem that existed in the water body gets disturbed.
Question 6.
What is the solution for air pollution caused by the vehicle’s emissions?
Answer:
Electric vehicles
Question 7.
Which are the chemical substances produced by the automobile emissions?
Answer:
When automobile engines are operated using fuels like petrol and diesel, sulphur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, carbon monoxide and particulate matter are released.
Question 8.
What is the purpose of smoke testing?
Answer:
Smoke testing is carried out to find out whether the smoke of vehicles contains more than the permissible amount of harmful chemical substances. By smoke testing, it can be detected whether vehicle emissions contain more harmful chemical substances due to engine failure, age of vehicles and impurities in fuel.
Question 9.
Why is it necessary to prevent the increased use of plastics?
Answer:
Plastics are non-degradable substances that pollute air, water, and soil. Burning plastic releases poisonotis gases, causing air pollution and irritation. Plastic doesn’t degrade in soil, preventing water; penetration and root growth. Mosquitoes multiply in plastic vessels, and stagnant water leads to the destruction of aquatic organisms. The treatment of plastic waste is a serious issue.
Question 10.
Explain the different methods for the purification of drinking water.
Answer:
Boiling for at least one minute will kill the microorganisms in the water. But the dissolved components in the water will remain.
Sifting:-Undissolved impurities in water are separated by filters.
Sedimentation:-The undissolved impurities are allowed to settle down. The water that appears on top can be separated and used.
Chlorination:-Adding a sufficient quantity of bleaching powder will kill the microorganisms in water.
Filtration:-It is the method of boiling water into steam and cooling it to collect pure water. There will be no dissolved components in the water collected in this way.
Hurt not the Environment Class 7 Notes
- The smoke and unbumt remains generated by burning wastes, including plastic, have an adverse impact on air, soil, water and living organisms.
- Air pollution is caused by the mixing of smoke, toxic gases and other chemical substances in the atmospheric air.
- Nitrogen is the most abundant component found in the atmosphere.
- Petrol, Diesel, CNG, and Electricity are commonly used as fuels in vehicles.
- Using public transport like buses and trains can help to reduce the need for private vehicles and thereby reduce pollution.
- Smoke testing is carried out to find out whether the smoke of vehicles contains more than the permissible amount of harmful chemical substances.
- Electric vehicles are a solution for air pollution caused by vehicles.
- Excess growth of water plants like algae in water bodies is caused by a phenomenon known as eutrophication.
- Reducing waste, recycling materials, and reusing products can help minimise the amount of waste.
- The drinking water can be purified using different techniques like Boiling, Sifting, Sedimentation, Chlorination, and Filtration.
- Vermicomposting, Air Contact Composting and Biogas Production are the different ways of scientific methods of waste management.