The comprehensive approach in SCERT Class 6 Basic Science Textbook Solutions Chapter 3 Let’s Stand Straight Important Questions ensure conceptual clarity.
Let’s Stand Straight Extra Questions and Answers Class 6 Basic Science Chapter 3 Kerala Syllabus
Let’s Stand Straight Class 6 Important Questions
Question 1.
How do skeletons help animals?
Answer:
- Provide shape and strength to the body.
- Help in movement.
Question 2.
What will happen if there is no skeleton?
Answer:
There would be no structures or shape to the body, and the individual would be unable to walk and run.
Question 3.
Why do birds have lighter skeletons compared to many other animals?
Answer:
Birds have lighter skeletons because their bones contain air cavities (empty spaces filled with air), which helps them fly.
![]()
Question 4.
Can you identify the animals to which these skeletons belong? Write down your answers.

Answer:
a) Hen
b) Lizard
c) Cow
Question 5.
Choose the correct statements from the following:
a. Birds have lighter skeletons compared to many other animals
b. Birds have air cavities in the bones
c. Birds have no air cavities
d. Birds have a harder skeleton
Answer:
a. Birds have lighter skeletons compared to many other animals,
b. Birds have air cavities in the bones
Question 6.
Choose the correct number of bones and complete the table
[33, 32, 22, 24]
| Skull | (a) |
| Ribs | (b) |
| Vertebral column | (c) |
| In each hand | (d) |
Answer:
(a) 22
(b) 24
(c) 33
(d) 32
Question 7.
Bones give shape and strength to our body. They also help in movement
a) Complete the table below.
| Ribs | 12 Pairs bend to form like a cage | (i) |
| Vertebral Column | (ii) | Helps to maintain an erect posture and facilitates body movement. |
| Bones in the hand | Small bones are joined in fingers. Long bones are seen in the arm and forearm. | (iii) |
| Bones in the leg | Big thigh bones. | (iv) |
b) Which is the biggest bone in the human body
Answer:
a) (i) Protects internal organs like the heart and lungs.
(ii) Made up of 33 small bones called vertebrae, arranged one above the other.
(iii) Helps to grasp and handle objects
(iv) Supports the weight of the body and enables locomotion (walking, running jumping, etc.)
b) Femur is the largest bone in human body.
Question 8.
Observe the picture.

A) Identify and write the bones marked a, b and c
B) Write the function of any two bones labelled in the skeleton.
C) The movable bone in the skull ……………………..
Answer:
A) a) Skull
b) Ribs cage
c) Femur
B) Skull: Protect the brain from injury
Ribs cage: Protects internal organs such as the heart and lungs.
C) Lower jawbone
Question 9.
It’s of different body parts, and their characteristics are listed below. Read them. Arrange the table in the correct order.
| Body parts | Joints | Characteristics |
| Knee | Pivot joint | Can be moved in many directions |
| Neck | Ball and socket joint | Can be moved in only one direction |
| Shoulder Joint | Hinge joint | Can be moved in both directions |
Answer:
| Body parts | Joints | Characteristics |
| Knee | Hinge joint | Can be moved in only one direction |
| Neck | Pivot joint | Can be moved in both directions |
| Shoulder Joint | Ball and socket joint | Can be moved in many directions |
![]()
Question 10.
Look at the picture of the joint

a) Identify the joint?
b) Write the procedure and material needed for making a model of this joint by using easily available objects.
c) Write the body parts in which the ball and socket joint is seen. Write their features?
Answer:
a) Ball and socket joint
b) Materials: 2 ice cream balls (big – 1, small – 1), Wooden scale – 2, Nuts and bolts – 2
Cut off a small part of the big ice cream ball in such a way that the small ice cream ball remains fitted inside it. Fix the two ice cream balls on the wooden scales using nuts and bolts, as shown in the picture. Hold the scale with the large ice cream ball in one hand and try rotating the scale with the small ice cream ball, It resembles the movement of the shoulder.

c) Shoulder joints, Hip joints
• The joint, with the maximum freedom of movement.
• The rounded end of one bone rotates in the cavity of another bone.
Question 11.
a) Identify the parts of the human skeleton given below

b) (i) Which parts of the skeleton protect the internal organs like the heart, brain, and spinal cord?
(ii) Write the peculiarity of any one part of the skeleton.
c) Which is the biggest bone in the human body
d) Which is the smallest bone in the human body
Answer:
a) Vertebral Column
b) (i) Skull: Protects the brain.
Rib Cage: Protects the heart and lungs.
Vertebral Column: Protects the spinal cord.
(ii) Ribs enfold and protect the heart, lungs, and some major blood vessels.
Ribs are strong and flexible
c) Femur is the largest bone
d) Stapes is the smallest bone in our body.
Question 12.
a) Which among the substances given below can be used to make a model of a pivot joint?
| Powder tin, small ball, Lids, Head of a doll, Hinges |
b) What will be the difficulties faced by us if there are no joints in our body?
c) Write the body parts in which Pivot joints is seen. Write their features.
Answer:
a) Powder tin, Head of a doll
b) We wouldn’t be able to bend, twist, or move any part of our body.
c) Neck
The bone that moves forward, backwards and side to side in another bone
Question 13.
Some activities are given below.
a) Rotates the arm in a circle.
b) Bending the knee to sit down
c) Turning the neck to look in both directions.

A) Write the names of the joints that help perform the activities listed above.
B) hat can we do before taking a person with a fracture to the hospital?
Answer:
A) a) Ball and socket joint
b) Hinge Joint
c) Pivot Joint
B)
- Don’t move the injured part
- Use a splint
- Apply Ice
- Seek medical help immediately.
Question 14.
Observe the Picture

A) W rite down the name of the major organ protected inside the skull.
B) How many bones are there in the Adult human body?
C) How many bones are there in Skull?
D) What are the main parts of Human skeleton
Answer:
A) Brain
B) 206
C) 22
D) The skull, vertebral column, ribs, rib cage, bones of the arms and legs, and hipbones together form the human skeleton.
Question 15.
A) What are cartilages?
B) Where are cartilages found in the human body?
Answer:
A) Cartilages are flexible parts that provide support and strength to the body, like bones. They are softer than bones and are found in both the human body and the bodies of other animals.
B) Primarily, cartilages are found in the ears, nose, elbows, knees, ankles, trachea and the discs between the vertebrae.
![]()
Question 16.
Write the necessity of wearing a helmet while travelling on two-wheelers.
Answer:
Reduce injuries
- Protect your head
- Protect your eyes and face from wind, dust, bugs, and little stones.
Question 17.
Which activity is not to be given to a person whose vertebral column is injured?
i. Protect the body part without movement
ii. Carry him on the shoulder
iii. Make him lie on a broad wood plank
Answer:
ii. Carry him on the shoulder
Question 18.
Your friend fell down during 9 football game and fractured his arm.

a) What first aid should be provided to someone with a fracture?
b) Why do we use the metal rod for fixing a fractured bone?
c) What nutrients and nutrient-rich foods should the child eat for strong bones, as advised by the doctor?
Answer:
a) Immobilise the Injured Area
- Bandage the injured part using a splint.
- Apply Cold (Ice Pack)
- A person with a bone fracture should be taken to the hospital immediately after receiving first aid.
b) It helps the bones to stay stable and heal quickly.
c) Calcium: The primary mineral component of bones, essential for bone formation and strength. Milk, yogurt, cheese, paneer, ragi, etc.
Vitamin D: Fatty fish, egg yolks, fortified milk, fortified cereals, and exposure to sunlight (the body produces Vitamin D when skin is exposed to sunlight).
Protein: provides the framework (collagen) onto which calcium and other minerals are deposited. Lean meats (chicken, fish), eggs, dairy products, pulses, etc.
Question 19.
A) What is a fracture?
B) How can a fracture be identified?
C) How many types of fractures are there? What are they?
Answer:
A) A fracture is the breaking or cracking of a bone.
B)
- Pain in the injured area.
- Difficulty in moving the injured part.
- Differences when compared with similar parts.
C)
- Fractures can occur in three ways.
- Simple Fracture: This is when a bone cracks, breaks, or dislocates but doesn’t pierce through the skin.
- Compound Fracture: The bone breaks and pierces through the skin and muscles, often causing open wounds.
- Complicated Fracture: This is a type of compound fracture where the broken bone injures nearby internal organs.
Question 20.
Observe the picture

Classify the given organisms based on their skeletons.
| (i) | Exoskeleton |
| (ii) | (iii) |
| Fish | (iv) |
Answer:
(i) Endoskeleton
(ii) House Lizards
(iii) Beetle
(iv) Snail
Question 21.
Observe the pictures

a) What is the difference between the skeletons of a cockroach and Lizard?
b) What are the similarities between endoskeleton and exoskeleton?
Answer:
a) Cockroaches have an exoskeleton, and lizards possess an endoskeleton.
b) Both skeletons provide structural support.
Both exoskeletons and endoskeletons allow animals to move about and protect their internal organs.
![]()
Question 22.
Classify the following organisms into those having an Endoskeleton, an Exoskeleton and both.
| Cockroach, Lizard, Turtle, Crocodile, Hen, Snail, Prawns, Crab, Centipede, Beetle, Birds, Cow, Cat, Dog |
Answer:
| Organism With an Endoskeleton | Organism with an Exoskeleton | An organism having both an exoskeleton and an endoskeleton |
| Lizard | Cockroach | Turtle |
| Hen | Snail | Crocodile |
| Birds | Prawns | |
| Cow | Crab | |
| Cat | Centipede | |
| Dog | Beetle |
Question 23.
Analyze the pictures and answer the following questions:
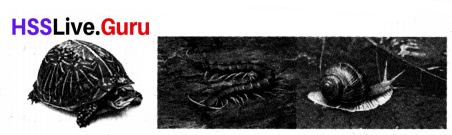
a) Name the type of skeleton present in this snail and centipede.
b) Name the organism that has both exoskeleton and endoskeleton.
c) How does the outer skeleton benefit the organisms
Answer:
a) Exoskeleton
b) Turtle
c) They help to protect and give shape to their body and offer protection from enemies.