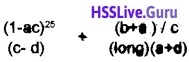Students can Download Chapter 1 Review of C++ Programming Questions and Answers, Plus Two Computer Application Chapter Wise Questions and Answers helps you to revise the complete Kerala State Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Kerala Plus Two Computer Application Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 1 Review of C++ Programming
Plus Two Computer Application Review of C++ Programming One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
IDE means ______
IDE _______.
Answer:
Integrated Development Environment.
Question 2.
We know that C++ is a high level language. From the following which statement is true.
(a) C++ contains English like statements.
(b) C++ contains mnemonics
(c) C++ contains only 0 and 1
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) C++ contains English like statements.

Question 3.
C++ is a_____language.
(a) High level
(b) Low level
(c) Middle level
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) High level.
Question 4.
C++ was developed at_______.
(a) AT & T Bell Laboratory
(b) Sanjose Laboratory
(c) Kansas University Lab
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) AT & T Bell Laboratory.
Question 5.
C++ is a successor of______language.
(a) C#
(b) C
(c) Java
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) C.

Question 6.
The most adopted and popular approach to write programs is_______.
Answer:
Structured programming.
Question 7.
From the following which uses OOP concept.
(a) C
(b) C++
(c) Pascal
(d) Fortran
Answer:
(b) C++.
Question 8.
_____is the smallest individual unit.
Answer:
Token
Question 9.
Pick the odd one out
(a) float
(b) void
(c) break
(d) Alvis
Answer:
(d) Alvis, the others are keywords.

Question 10.
Reserved words for the compiler is_______.
(a) Literals
(b) Identifier
(c) Keywords
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Key words.
Question 11.
Pick an identifier from the following.
(а) auto
(b) age
(c) float
(d) double
Answer:
(b) age.
Question 12.
Pick the invalid identifier
(a) name
(b) Date of birth
(c) age
(d) joining_time
Answer:
(b) Date of birth, because it contains space.

Question 13.
Pick the octal integer from the following.
(a) 217
(b) 0 × 217
(c) 0217
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) 0217, an octal integer precedes 0.
Question 14.
Pick the hexa decimal integer from the following.
(а) 217
(b) 0 × 217
(c) 0217
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) 0 × 217, an hexa decimal integer precedes Ox.
Question 15.
From the following pick a character constant.
(a) ’A’
(b) ‘ALL’
(c) ‘AIM’
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) ‘A’, a character enclosed between single quote.

Question 16.
Non graphic symbol can be represented by using______
Answer:
Escape Sequence.
Question 17.
Manish wants to write a program to produce a beep sound. Which escape sequence is used to get an alert (sound).
(a) \a
(b) \d
(c) \s
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) \a.
Question 18.
Ajo wants to print a matter in a new line. Which es-cape sequence is used for this?
(a) \a
(b) \n
(c) \s
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) \n.
Question 19.
To represent null character______is used
(a) \n
(b) \0
(c) \f
(d) \s
Answer:
(b) \0.
Question 20.
State True/False a string is automatically appended by a null character.
Answer:
True.

Question 21.
From the following pick a string constant.
(a) ‘a’
(b) “abc”
(c) ‘abc’
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) “abc”, a character constant must be enclosed between double quotes.
Question 22.
C++ was developed by______
(a) Bjarne Stroustrup
(b) James Gosling
(c) Pascal
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Bjarne Stroustrup.
Question 23.
From the following which is not a character constant.
а) ‘c’
b) ‘e’
c) ‘d’
d) “c”
Answer:
(d) “c”, It is a string constant the others are character constant.
Question 24.
From the following which is a valid declaration.
(a) int 91;
(b) int x;
(c) int 9x;
(d) int “x”;
Answer:
(b) int x;
Question 25.
Symbols used to perform an operation is called_______
(a) Operand
(b) Operator
(c) Variable
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Operator.

Question 26.
Consider the following. C = A + B. Here A and Bare called______
(a) Operand
(b) Operator
(c) Variable
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Operand.
Question 27.
The. execution of a program starts at_______function.
Answer:
main()
Question 28.
The execution of a program ends with______function
Answer:
main()
Question 29.
______USed to write single line comment
(a) //
(b) /*
(c) */
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) //
Question 30.
const k = 100 means const k = 100
(a) const float k = 100
(b) const double k = 100
(c) const int k = 100
(d) const chark = 100
Answer:
(c) const int k = 100

Question 31.
Each and every statement in C++ must be end with_____
(а) Semi colon
(b) Colon
(c) full stop
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Semi colon
Question 32.
From the following select the input operator.
(a) >>
(b) <<
(c) >
(d) <
Answer:
(a) >>
Question 33.
From the following select the output operator.
(a) >>
(b) <<
(c) >
(d) <
Answer:
(b) <<
Question 34.
In while loop, the loop variable should be updated?
(a) along with while statement
(b) after the while statement
(c) before the while statement
(d) inside the body of while
Answer:
(d) Inside the body of while

Question 35.
Adeline wrote a C++ program namely sum.cpp and she compiled the program successfully with no error. Some files are generated. From the following which file is a must to run the program
(a) sum.exe
(b) sum.obj
(c) sum.vbp
(d) sum.htm
Answer:
(a) sum.exe
Question 36.
Adeline wrote a C++ program namely sum.cpp and she compiled the program successfully with no error. Some files are generated namely sum.obj and sum.exe. From this which file is not needed to run the program
Answer:
sum.obj is not needed and can be deleted.
Question 37.
To terminate a program, from the following which is used.
(a) break
(b) continue
(c) end()
(d) exit()
Answer:
(d) exit()
Question 38.
To write a C++ program, from the following which statement is a must.
(a) sum()
(b) main()
(c) #include
(d) #include
Answer:
(b) main(). A C++ program must contains at least one main() function.
Question 39.
State True / False. Comment statements are ignored by the compiler
Answer:
True.
Question 40.
More than one input / output operator in a single statement is called______.
Answer:
Cascading of I/O operator.

Question 41.
From the following which is ignored by the compiler.
(a) statement
(b) comments
(c) loops
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) comments
Question 42.
From the following which is known as string terminator
(a) ‘\0’
(b) ‘\a’
(c) *\s*
(d) ‘\t’
Answer:
(a) ‘\0’
Question 43.
______is the main activity carried out in computers.
Answer:
Data processing.
Question 44.
The data used in computers are different. To differentiate the nature and size of data______is used.
Answer:
Data types.
Question 45.
Classify the following data types.
- int
- array
- function
- char
- pointer
- void
- float
- double
- structure
Answer:
| Fundamental data types |
Derived data types |
| int |
array |
| float |
function |
| double |
pointer |
| void |
structure |
| char |
|
Question 46.
Sheela wants to store her age. From the following which is the exact data type.
(a) void
(b) char
(c) int
(d) double
Answer:
(c) int

Question 47.
Integer data type uses_____bytes of memory
(a) 5
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer:
(b) 2
Question 48.
char data type uses______bytes of memory
(a) 1
(b) 3
(c) 7
(d) 8
Answer:
(a) 1
Question 49.
From the following which data type uses 4 bytes of memory
(a) float
(b) short
(c) char
(d) double
Answer:
(a) float
Question 50.
Full form of ASCII is______.
Answer:
American Standard Code for Information Interchange.
Question 51.
Ramu wants to store the value of From the following which is correct declaration
(а) char pi = 3.14157
(b) int pi = 3.14157
(c) float pi = 3.14157
(d) long pi = 3.14157
Answer:
(c) float pi = 3.14157.

Question 52.
From the following which is not true, to give a variable name.
(a) Starting letter must be an alphabet
(b) contains digits
(c) Cannot be a key word
(d) special characters can be used
Answer:
(d) special characters can be used
Question 53.
Pick a valid variable name from the following
(а) 9a
(b) float
(c) age
(d) date of birth
Answer:
(c) age
Question 54.
To perform a unary operation how many number of operands needed?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 1
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) 1 (Unary means one)
Question 55.
To perform a binary operation how many number of operands needed?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 1
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) 2 (binary means two)

Question 56.
To perform a ternary operation how many number of operands needed?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 1
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) 3(eg: ternary means three)
Question 57.
In C++ 13 % 26 =_______
(a) 26
(b) 13
(c) 0
(d) None of these
Answer:
13. % is a mod operator i.e. it gives the remainder. Here the remainder is 13.
Question 58.
In C++ 41/2 =______
(a) 20.5
(b) 20
(c) 1
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) 20. (The actual result is 20.5 but both 41 and 2 are integers so .5 must be truncated).
Question 59.
++ is a_____operator
(a) Unary
(b) Binary
(c) Ternary
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Unary.
Question 60.
Conditional operator is______operator
(a) Unary
(b) Binary
(c) Ternary
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Ternary

Question 61.
% is a_____operator
(a) Unary
(b) Binary
(c) Ternary
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Binary
Question 62.
State True/False
- Multiplication, division, modulus have equal priority
- Logical and (&&) has less priority than logical or ()
Answer:
- True
- False
Question 63.
______is composed of operators and operands
(a) expression
(b) Key words
(c) Identifier
(d) Punctuators
Answer:
(a) expression
Question 64.
Supply value to a variable at the time of declaration is known as______.
Answer:
Initialisation.
Question 65.
From the following which is initialisation
(a) int k;
(b) int k = 100;
(c) int k[10];
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) int k= 100;

Question 66.
State True/False
In an expression, aH the operands having lower size are converted(promoted) to the data type of the highest sized operand.
Answer:
True
Question 67.
Classify the following as arithmetic / Logical expression.
(a) x + y * z
(b) x < y && y > z
(c) x/y
(d) x > 89 || y < 80
Answer:
(a) and (c) are Arithmetic
(b) and (d) are Logical
Question 68.
Suppose x = 5 and y = 2 then what will be count << (float) x/y.
Answer:
2.5 The integer x is converted to float hence the result.
Question 69.
Considerthe following ,
a = 10; a* = 10;
Then a =______
(a) a = 100
(b) a = 50
(c) a = 10
(d) a = 20
Answer:
(a) a = 100, This short hand means a = a * 10
Question 70.
Consider the following a = 10; a+ = 10; Then a =_____
(a) a = 30
(b) a = 50
(c) a = 10
(d) a = 20
Answer:
(d) a = 20. This short hand means a = a + 10.

Question 71.
Pick the odd one out
(a) structure
(b) Array
(c) Pointer
(d) int
Answer:
(d) int, it is fundamental data type the others are derived data types.
Question 72.
From the following select not a character of C++ language
(a) A
(b) 9
(c) \
(d) @
Answer:
(d) @
Question 73.
Consider the following float x = 25.56; cout << (int)x;
Here the data type of the variable is converted. What type of conversion is this?
(a) type promotion
(b) type casting
(c) implicit conversion
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) type casting (explicit conversion);
Question 74.
From the following which is ignored by the compiler
(a) statement
(b) comments
(c) loops
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) comments
Question 75.
Multi line comment starts with____and ends with_____
(a) /’ and ‘/
(b) */ and /*
(c) /* and */
(d) ‘/ and /’
Answer:
(c) /* and */

Question 76.
Single line comment starts with_____
(a) **
(b) @@
(c) */
(d) //
Answer:
(d) //
Question 77.
Alvin wants to store the value of π From the following which is correct declaration
(a) char pi = 3.14157
(b) const int pi = 3.14157
(c) const float pi = 3.14157
(d) long pi = 3.14157
Answer:
(c) const float pi = 3.14157
Question 78.
To store 70000 which modifier is used with int.
(a) long
(b) short
(c) big
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) long
Question 79.
To store 60000 which modifier is used with int.
(a) unsigned
(b) short
(c) big
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) unsigned
Question 80.
Consider x++(post fix form). Select the correct definition from the following
(a) The operation is performed after the value is used
(b) The operation is performed before the value is used
(c) First change then use
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) The operation is performed after the value is used

Question 81.
Consider ++x(pre fix form). Select the correct definition from the following
(a) The operation is performed after the value is used
(b) The operation is performed before the value is used
(c) First use then change
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) The operation is performed before the value is used
Question 82.
Consider the following int a = 10; float b = 4; cout << a/b; We know that the result is 2.5 a float. What type of conversion is this?
(a) type promotion
(b) type casting
(c) explicit coversion
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) type promotion (implicit conversion);
Question 83.
From the following which has the major priority?
(а) ++
(b) =
(c) ==
(d) &&
Answer:
(a) ++
Question 84.
One of your friend told you that post increment (eg:x++) has more priority than pre increment (eg: ++x). State True/False
Answer:
It is true.
Question 85.
Raju declared a variable as follows. unsigned number;
So he can a store a number in the range______
(a) 0 to 65535
(b) -32768 to 32767
(c) 0 to 65536
(d) 0 to 95536
Answer:
(a) 0 to 65535. Unsigned uses only 2 bytes of memory but no negative numbers can store.

Question 86.
Considerthe following declaration. signed number;
So we can a store a number in the range______
(a) 0 to 65535
(b) -32768 to 32767
(c) 0 to 65536
(d) 0 to 95536
Answer:
(b) -32768 to 32767
Question 87.
Pick the odd one out
(a) long
(b) short
(c) unsigned
(d) int
Answer:
(d) int. It is fundamental type modifiers.
Question 88.
Memory size and sign can be changed using______with fundamental data types.
Answer:
Type modifiers.
Question 89.
“Its value does not change during execution”. What is it?
Answer:
Constant.
Question 90.
“BVMHSS” is called______
(a) integer constant
(b) float constant
(c) string constant
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) string constant

Question 91.
The address of a variable is called______
Answer:
L-value (Location value) of a variable.
Question 92.
The content of a variable is called_______
Answer:
R-value (Read value) of a variable.
Question 93.
Suppose the address of a variable age is 1001 and the content i.e. age = 33. Then what is R-value and L-value?
Answer:
R-value is 33 and L-value is 1001.
Question 94.
A total of 65535 single window +1 application forms are sold in a district. To store the application form, from the following which is valid?
(a) unsigned app_no;
(b) intapp_no;
(c) signed app_no;
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) unsigned app_no;
Question 95.
is it possible to declare a variable as and when a need arise. What kind of declaration is this?
Answer:
Yes. It is known as Dynamic declaration.
Question 96.
Emerin wants to store a constant value. Which key word is used for this?
Answer:
constant.
Question 97.
Suppose x = 5. Then cout << x++ displays_____
Answer:
5. Here post increment first use the value then incremented.

Question 98.
Suppose x = 5. Then cout << ++x displays_____
Answer:
6. Here pre increment first incremented and then use the value.
Question 99.
An if statement contains another if statement completely. Then it is known as______
Answer:
Nested if
Question 100.
From the following which is not optional with switch statement.
Answer:
(a) break
(b) default
(c) case
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) case.
Question 101.
To exit from a switch statement______is used
(a) quit
(b) exit
(c) break
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) break
Question 102.
From the following which statement is true for switch statement
(a) switch is used to test the equality
(b) switch is used to test relational or logical expression
(c) switch can handle real numbers case data
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) switch is used to test the equality
Question 103.
Sonet wants to execute a statement more than once. From the following which is exactly suitable.
(a) if
(b) loop
(c) switch
(d) if-else if ladder
Answer:
(b) loop

Question 104.
Odd one out
(a) for
(b) if
(c) switch
(d) if-else if ladder
Answer:
(a) for. It is a loop the others are branching statement
Question 105.
Odd one out
(a) for
(b) if
(c) while
(d) do while
Answer:
(b) if. It is a branching statement and the others are loops.
Question 106.
From the following which loop does the three things, initialisation, checking, and updation.
(a) while
(b) do while
(c) for
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) for
Question 107.
Predict the output for(i=1;i<=10;i++); cout<<i;
(a) 10
(b) 1 to 10.
(c) 11
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) 11.

Question 108.
From the following which is exit controlled loop
(a) for
(b) while
(c) do while
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) do while
Question 109.
_____statement is used for unconditional jump from one location to another.
Answer:
goto.
Question 110.
Sunitha wants to skip one iteration. From the following which will help her?
(a) continue
(b) break
(c) for
(d) case
Answer:
(a) continue.
Question 111.
Pick the odd one out from the following. Give reason
1. (a) for
(b) while
(c) do____while
2. (a) if
(b) switch
(c) for
Answer:
- do_____while . It is an exit controlled loop others are entry controlled loop
- for. It is a loop while others are branching statements.

Question 112.
Identify the error in the following C++ statement and correct it. short population = 68000;
Answer:
The maximum number that can store in short type is less than 32767. So to store 68000 we have to use long data type.
Question 113.
What would be the appropriate data type to store the following?
- Number of students in a classroom
- Age of a student
- Average mark of a student
- A question mark (?)
Answer:
- short or int
- short or int
- float
- char
Question 114.
Pick odd one out from the following loops. Give the reasons.
(a) for
(b) while
(c) do___while
Answer:
(c) do while. This is an exit controlled loop others are entry controlled loop.
Question 115.
Which of the following data types of C++ has no type modifier?
(a) void
(b) int
(c) char
(d) short
Answer:
(a) void
Plus Two Computer Application Review of C++ Programming Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Mr. Dixon declared a variable as follows
int 9 age. Is it a valid identifier. If not briefly explain the rules for naming an identifier.
Answer:
It is not a valid identifier because it violates the rule 1. The rules for naming an identifier is as follows.
- It must be start with a letter(alphabet)
- Underscore can be considered as a letter
- White spaces and special characters cannot be used.
- Key words cannot be considered as an identifier

Question 2.
Rose wants to print as follows \n is used for New Line
Write down the C++ statement for the same.
Answer:
# include
using namespace std;
{
cout<<“\\n is used for New Line”;
}
Question 3.
Alvis wants to give some space using escape sequence as follows
Welcome to C++
Write down the C++ statement for the same
Answer:
# include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout<<“welcome to \t C++”;
}
Question 4.
How many bytes used to store ‘\a’.
Answer:
To store ‘\a’ one byte is used because it is an escape sequence. An escape sequence is treated as one character. To store one character one byte is used.
Question 5.
How many bytes used to store “\abc”.
Answer:
A string is automatically appended by a null character.
Here one byte for \a(escape sequence).
One byte for character b.
One byte for character c.
And one byte for null character.
So a total of 4 bytes needed to store this string.
Question 6.
How many bytes used to store “abc”.
Answer:
A string is automatically appended by a null character.
Here one byte for a.
One byte for character b.
One byte for character c.
And one byte for null character.
So a total of 4 bytes needed to store this string.

Question 7.
We know that the value of pi = 3.14157, a constant (literal). What is a constant? Explain it?
Answer:
A constant ora literal is a data item its value doe not change during execution.
1. Integer literals:
Whole numbers without fractional parts are known as integer literals, its value does not change during execution. There are 3 types decimal, octal, and hexadecimal.
Eg. For decimal 100,150,etc
For octal 0100,0240, etc
For hexadecimal 0 × 100, 0 × 1 A, etc
2. Float literals:
A number with fractional parts and its value does not change during execution is called floating-point literals.
Eg. 3.14157,79.78,etc.
3. Character literal:
A valid C++ character enclosed in single.
Question 8.
Write a program to print the message “TOBACCO CAUSES CANCER” on screen.
Answer:
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout<<“TOBACCO CAUSES CANCER”;
}

Question 9.
Consider the following code
int main()
{
cout<<“welcome to C++”;
}
After you compile this program there is an error called prototype error. Why it is happened? Explain Answer:
Here we used the output operator cout<<. It is used to display a message “welcome to C++” to use this operator the corresponding header file must be included and using namespace std; is also include. We didn’t included the header file hence the error.
Question 10.
You are supplied with a list of tokens in C++ program, Classify and Categorise them under proper headings. Explain each category with its features. tot_mark, age, M5,_____break,(), int, _pay, ; , cin
Answer:

Question 11.
In C++ the size of the string “book” is 5 and that of “book\n” is 6. Check the validity of the above statement. Justify your answer.
Answer:
A string is automatically added by a null character(\0). The null character is treated as one character. So the size of string “book” is 5. Similarly, a null character (\0) is also added to “book\n”. \n and \0 is treated as single characters. Hence the size of the string “book\n” is 6.
Question 12.
Is 0 × 85B a valid integer constant in C++? If yes why?
Answer:
Yes. It is a hexa decimal number.
Question 13.
Pick the odd man out. Justify
TOTSAL, TOT_SAL, totsal5, Tot5_sal, SALTOT, tot.sal
Answer:
tot.sal. Because it contains a special character dot(.). An identifier cannot contain a special character. So it is not an identifier. The remaining satisfies the rules of naming identifier. So they are valid identifier.
Question 14.
Write a C++ statement to print the following sentence. Justify “\ is a special character”
Answer:
- cout<<“\\ is a special character”
- \\ is treated as an escape sequence.

Question 15.
A student type a C++ program and saves it in his personal folder as Sample.cpp. After getting the output of the program, he checks the folder and finds three files namely Sample.cpp, Sample.obj and Sample.exe. Write the reasons for the generation of the two files in the folder.
Answer:
After the compilation of the program sample.cpp, the operating system creates two files if there is no error. The files are one object file (sample.obj) and one executable file(sample.exe). Now the source file(sample.cpp) and object file(sample.obj) are not needed and can be deleted. To run the program sample.exe is only needed.
Question 16.
Write a program to print the message “SMOKING IS INJURIOUS TO HEALTH” on screen.
Answer:
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout<<” SMOKING IS INJURIOUS TO HEALTH”;
}
Question 17.
Consider the following
short number;
number = 76543;
Is it valid. Explain?
Answer:
It is not valid. Because the data type int uses only two bytes(16 bits) of memory. That is we can store a total of 216 = 65536 integers. There are 2 types of integers negative integers and positive integers, i.e. 32768 each.
So we can store a number in between -32768 to +32767 (0 included in the positive section). The number 76543 is bigger than this range. Hence there is an error overflow. To store this number declare the variable is as follows.
long number;

Question 18.
Consider the following declaration.
const int bp;
bp = 100;
Is it valid? Explain it?
Answer:
This is not valid. This is an error. A constant variable cannot be modified. That is the error and a constant variable must be initialised. So the correct declaration is as follows, const int bp = 100;
Question 19.
Consider the following statements in C++
- cout<<41/2;
- cout<<41/2.0;
Are this two statements give same result? Explain?
Answer:
This two statements do not give same results. The first statement 41/2 gives 20 instead of 20.5. The reason is 41 and 2 are integers. If two operands are integers the result must be integer, the real part must be truncated.
To get floating result either one of the operand must be float. So the second statement gives 20.5. The reason is 41 is integer but 2.0 is a float.
Question 20.
If mark = 70 then what will be the value of variable result in the following result = mark > 50? ‘P’: ‘F’;
Answer:
The syntax of the conditional operator is given below Condition? Value if true: Value if false; Here the conditional operator first checks the condition i.e.,70 > 50 it is true. So ‘P’ is assigned to the variable result. So the result is d ‘P’;
Question 21.
Is it possible to initialise a variable at the time of execution. What kind of initialisation is this? Give an example.
Answer:
Yes it is possible. This is known as Dynamic initialisation. The example is given below
Eg: int a=10, b=5;
int c = a*b;
here the variable c is declared and initialised with the value 10*5.

Question 22.
Boolean data type is used to store True / False in C++. Is it true? Is there any data type called Boolean in C++?
Answer:
No there is no data type for storing boolean value true /false. But in C++ non -zero (either negative or positive) is treated as true and zero is treated as false.
Question 23.
Consider the following
n=-15;
if (n)
cout<<“Hello”;
else
cout<<“hai”;
What will be the output of the above code?
Answer:
The output is Hello, because n = -15 a non zero number and it is treated as true hence the result.
Question 24.
Is it possible to declare a variable in between the program as and when the need arise? Then what is it?
Answer:
Yes it is possible to declare a variable in between the program as and when the need arise. It is known as dynamic initialisation.
Eg. int x=10, y=20;
_____
_____
int z=x*y;
Question 25.
charch;
cout<<“Enter a character”; cin>>ch;
Considerthe above code, a user gives 9 to the variable ‘ch’. Is there any problem? Is it valid?
Answer:
There is no problem and it is valid since 9 is a character. Any symbol from the key board is treated as a character.

Question 26.
“With the same size we can change the sign and range of data”. Comment on this statement.
Answer:
With the help of type modifiers we can change the sign and range of data with same size. The important modifiers are signed, unsigned, long and short.
Question 27.
Write short notes about C++ short hands?
Answer:
x = x + 10 can be represented as x+=10, It is called short hands in C++. It is faster. This is used with all the arithmetic operators as follows.
| Arithmetic Assignment Expression |
Equivalent Arithmetic Expression |
| x+ = 10 |
x = x + 10 |
| x- = 10 |
x = x -10 |
| x* = 10 |
x = x * 10 |
| x/ = 10 |
x = x /10 |
| x% = 10 |
x = x % 10 |
Question 28.
What is the role of ‘const’ modifier?
Answer:
This ‘const’ key word is used to declare a constant. Eg. const int bp = 100; By this the variable bp is treated as constant and cannot be possible to change its value during execution.
Question 29.
Specify the most appropriate data type for handling the following data.
- Rollno. of a student.
- Name of an employee.
- Price of an article.
- Marks of 12 subjects
Answer:
- short Rollno;
- charname[20];
- float price;
- short marks[12];
Question 30.
Write C++ statement for the following.
- The result obtained when 5 is divided by 2.
- The remainder obtained when 5 is divided by 2.
Answer:
- 5/2
- 5%2
Question 31.
Predict the output of the following code. Justify.
int k = 5, b = 0;
b = k++ + ++k;
cout<<b; (2 Scores)
Answer:
Output is 12. In this statement first it take the value of k in 5 then increment it K++. So first operand for + is 5. Then it becomes 6. Then ++k makes it 7. This is the second operand. Hence the result is 12.

Question 32.
Predict the output.
- int sum = 10, ctr= 5;
sum = sum + ctr __;
cout<<sum;
- int sum = 10, ctr = 5;
sum = sum + ++ctr; court<<sum;
Answer:
- 15
- 16
Question 33.
Predict the output
int a;
float b;
a = 5;
cout<<sizeof(a + b/2);
Answer:
Output is 4. Result will be the memory size of floating point number.
Question 34.
Predict the output.
int a, b, c;
a = 5; b = 2;
c = a/b;
cout<<c;
Answer:
Output is 2. Both operands are integers. So the result will be an integer.
Question 35.
Explain cascading of i/o operations.
Answer:
The multiple use of input or output operators in a single statement is called cascading of i/o operators. Eg: To take three numbers by using one statement is as follows cin>>x>>y>>z; To print three numbers by using one statement is as follows. cout<<x<<y<<z;

Question 36.
Trace out and correct the errors in the following code fragments
- cout<<“Mark=”45;
- cin<<“HellowWorld!”;
- cout>>”X + Y;
- Cout<<‘Good'<<‘Moming’
Answer:
- cout<<“Mark=45”;
- cout<<“HellowWorld!”;
- cout<<X + Y
- Cout<<“Good Morning”;
Question 37.
What do you mean by preprocessor directive?
Answer:
A C++ program starts with the preprocessor directive i.e., #include, #define, #undef, etc, are such a preprocessor directives. By using #include we can link the header files that are needed to use the functions. By using #define we can define some constants.
Eg. #definex100. Here the value of x becomes 100 and cannot be changed in the program.
Question 38
Write a program to print a message as ” Hello, Welcome to C++”.
Answer:
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout<<” Hello, Welcome to C++”;
}
Question 39.
Write a program to generate the following table.
| 2013 |
100% |
| 2012 |
99.9% |
| 2011 |
95.5% |
| 2010 |
90.81% |
| 2009 |
85% |
Use a single cout statement for output
Answer:
# include
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
cout<<“2013\t 100%\n2012\t99.9%\n2011\t95.5%\n2010\t90.81%\n2009\t85%”;
}

Question 40.
Determine the data type of the following expression If a is an int, b is a float, c is a long int and d is a double
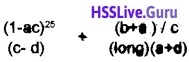
Answer:
In type promotion the operands with tower data type will be converted to the highest data type in the expression. So consider the following,

= double + long
= double (Which is the highest data type).
Question 41.
White writing a program Geo uses while loop but forgets to update the loop variable. What will happen?
Answer:
The loop variable inside the while loop must be updated otherwise the loop will not be terminated. The loop will be work infinitely.
Question 42.
Draw the flow chart of if statement.
Answer:
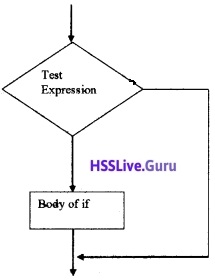
Question 43.
Draw the flow chart of if else statement.
Answer:
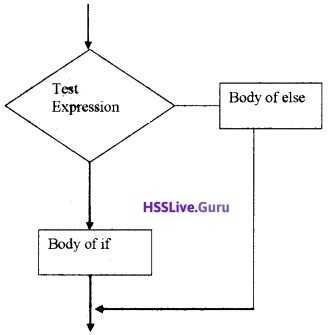

Question 44.
Write a while loop that display numbers from 500 to 550.
Answer:
int i=500
while (i<=550)
{
cout<<i;
i=i+1;
}
Question 45.
Compare if else and conditional operator?
Answer:
We can use conditional operator as an alternative of if-else statement. The conditional operator is a ternary operator.
The syntax of if-else
if (expression 1)
expression 2;
else
expression 3;
First expression 1 is evaluated if it is true expression 2 will be executed otherwise expression 3 will be executed. Instead of this, we can be written as follows using conditional operator Expression 1? expression 2: expressions;
Question 46.
Draw the flow chart of for loop.
Answer:
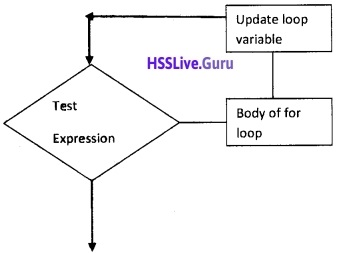

Question 47.
Find out the error in syntax if any and correct it? esm<oi!Bl

Answer:
a) No need of semi colon. The corrected loop is given below
while (test condition)
{
}
b) In do____white loop the while must be end with; semicoion.
do (condition)
{
}while;
c) switch contains expression instead of condition switch(expression)
{
Case 1:
Case 2:
Case 3:
Case 4:
}
Question 48.
State whether the following statements are True or False. In either case Justify your answer
- Break statements essential in switch
- For loop is an entry controlled loop
- Do____white loop is an entry controlled loop
- Switch is a selection statement
Answer:
- False. It is not essential in single case statement
- True. Because it will first check the condition. If it is true then only the body will be executed.
- False. It is an exit controlled loop.
- True.

Question 49.
Given a code segment for(i=1; i<10; i++) cout<<i;
- Rewrite the code using do____while loop
- What will be the output when i=0? Give reason.
Answer:
1. i=1;
do{
cout<<i;
i++;
}while(i<10);
2. When i=0, it will execute one more time. ie. the for loop execute 9 times but here this loop executes 10 times.
Question 50.
Write the equivalent code for the following statement R=(P<Q?P: Q)
Answer:
if(P<Q)
R=P;
else
R=Q;
Question 51.
Examine the following code snippet and find out the output? What will happen if the statement int ch; is replaced char ch;
int ch;
for(ch=’A’;ch<=’Z’;++ch)
cout<<ch<<”;
Answer:
This code snippet will print 65, 66, 67, ______,90. If the statement int ch; is replaced by char ch; it prints A, B, C,_____,Z.
Question 52.
Your friend usee the following identifiers in a program. Find out the invalid identifiers with reason if not valid, basic pay area, data-of-birth, B3, 9A, switch
Answer:
basic pay – Invalid because white space is not allowed.
area – valid
date-of-birth – Invalid because hyphen(-) is not allowed.
B3 – Valid
9A – Invalid because should not begin with number.
switch – Invalid because keywords not allowed.

Question 53.
int x=5;
int y=10;
cout<<(x+y)%2;
Answer:
(x+y) % 2 = (5+10)%2 = 15% 2 =1 It prints 1.
Question 54.
Classify the following C++ tokens in accordance to the table given below.

Answer:
keyword: int, do
Identifier: digit, cin(pre defined identifier, eg. int cin; is possible);
Literal: “break”(string literal), 25.6(float literal).
Operator: %(Mod operator), = (assignment operator).
Question 55.
Rewrite the following C++ code using conditional operator.
if (a>b)
max=a;
else
max=b;
Answer:
max=(a>b)?a:b;
Question 56.
Write the C++ expression to calculate the value of the following expression.
- x = \(\frac{\left(b^{2}-4 a c\right)}{2 a}\)
- y = a2 + 2ab + b2
Answer:
- x= (b*b – 4*a*c)/(2*a);
- y= a*a + 2*a*b + b*b;
Question 57.
Consider the following code and predict the output. Justify your answer.
for(int i=i;i<10;++i)

Answer:
The output is 1 2 3 4 5 6 7. This loop is used to print 1 to 10 but this loop will terminate when the value of i becomes 8. Hence it prints 1 to 7.

Question 58.
Predict the output for the following program code.
for(i=1;i<=10;++i)
{
if (i==7)
coutinue;
cout<<“\t”;
cout<< i;
}
Answer:
The output is 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 9 10.
This loop is used to print 1 to 10 but this loop will by pass one iteration when the value of i becomes 7. Hence it prints 1 to 10 except 7.
Question 59.
How many times the following loop will be executed?
int s = 0, i = 0;
do
{
S+= i;
i++;
} while(i < = 5);
Answer:
This loop will be executed 6 times. The value of i becomes 1 to 6.
Plus Two Computer Application Review of C++ Programming Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
In a panchayath or municipality, all the houses have a house number, house name, and members. Similar situation is in the case of memory. Explain.
Answer:
The named memory locations are called variable. A variable has three important things
- variable name: A variable should have a name
- Memory address: Each and every byte of memory has an address. It is also called location (L) value
- Content: The value stored in a variable is called content.lt is also called Read(R) value.

Question 2.
Briefly explain constants
Answer:
A constant or a literal is a data item its value doe not change during execution. The keyword const is used to declare a constant. Its declaration is as follows
const data type variable name=value;
eg.const int bp = 100;
const float pi = 3.14157;
const char ch = ‘a’;
const char[] = “Alvis”;
1. Integer literals:
Whole numbers without fractional parts are known as integer literals, its value does not change during execution. There are 3 types decimal, octal, and hexadecimal.
Eg. For decimal 100,150,etc
For octal 0100,0240, etc
For hexadecimal 0 × 100, 0 × 1A,etc.
2. Float literals:
A number with fractional parts and its value does not change during execution is called floating point literals.
Eg. 3.14157,79.78,etc.
3. Character literal:
A valid C++ character enclosed in single quotes, its value does not change during execution.
Eg. ‘m’, ‘f, etc.
4. String literal:
One or more characters enclosed in double quotes is called string constant. A string is automatically appended by a null charater(‘\0’)
Eg. “Mary’s”,”India”,etc.
Question 3.
Considerthe following statements
int a=10, x=20;
float b=49000.34, y=56.78;
- a=b;
- y=x;
Is there any problem for the above statements? What do you mean by type compatibility?
Answer:
Assignment operator is used to assign the value of RHS to LHS. Following are the two chances
- The size of RHS is less than LHS. So there is no problem and RHS data type is promoted to LHS. Here it is compatible.
- The size of RHS is higher than LHS. Here comes the problem sometimes LHS cannot possible to assign RHS. There may be a chance of wrong answer. Here it is not compatible.
Here
- a=b; There is an error since the size of LHS is 2 but the size of RHS is 4.
- y=x; There is no problem because the size of LHS is 4 and RHS is 2.

Question 4.
A company has decided to give incentives to their salesman as per the sales. The criteria is given below.
If the total sales exceeds 10,000 the incentive is 10%
- If the total sales >=5,000 and total sales <10,000, the incentive is 6 %
- If the total sales >=1,000 and total sales <5,000, the incentive is 3 %
Write a C++ program to solve the above problem and print the incentive after accepting the total sales of a salesman. The program code should not make use of if statement.
Answer:
# include
using namespace std;
int main()

Question 5.
A C++ program code is given below to find the value of X using the expression
X = \(\frac{a^{2}+b^{2}}{2 a}\) where a and b are variables 2a
# include
using namespace std;
int main()

Pre did the type of errors during compilation, execution, and verification of the output. Also write the output of two sets of input values
- a=4, b=8
- a=0, b=2
Answer:
This program contains some errors and the correct program is as follows.
#include
using namespace std;
int main()

The output is as follows
- a=4 and b= 8 then the output is 10
- a=0 and b= 2 then the output is an error divide by zero error(run time error).

Question 6.
We know that a program has a structure. Explain the structure of C++ program.
Answer:
A typical C++ program would contain four sections as shown below.
Include files
Function declarations
Function definitions
Main function programs
Eg.
# include
using namespace std;
int sum(int x, int y)
{return (x+y);}
int main()
{
cout<<sum(2,3);
}
}
Question 7.
Write a program to read two numbers and find its sum.
Answer:
#include
using namespace std;
int main()

Question 8.
Write a program to read three scores and find the average.
Answer:
#include
using namespace std;
int main()

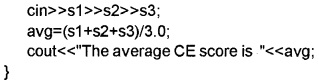
Question 9.
Write a program to find the area and perimeter of a circle.
Answer:
#include
using namespace std;
int main()


Question 10.
Write a program to find the simple interest
Answer:
# include
using namespace std;
int main()

Question 11.
Write a program to convert temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit.
Answer:
# include
using namespace std;
int main()

Question 12.
Write a program to read weight in grams and convert it into Kilogram.
Answer:
# include
using namespace std;
int main()


Question 13.
Write a program to read your height in meter and cm convert it into Feet and inches
Answer:
# include
using namespace std;
int main()

Question 14.
Write a program to find the area of a triangle.
Answer:
# include
using namespace std;
int main()

Question 15.
Write a program to
- print ASCII for a given digit.
- print ASCII for backspace.
Answer:
# include
using namespace std;
int main()


Question 16.
Write a program to read time in seconds and convert it into hours, minutes and seconds.
Answer:
# include
using namespace std;
int main()

Question 17.
Two pairs C++ expressions are given below.
- a=10, a==10
- b=a++, b=++a
- How do they differ?
- What will be the effect of the expression
Answer:
1. = is an assignment operator that assigns a value 10 to the LHS (Left Hand Side)variable a But == is equality operator that checks whether the LHS and RHS are equal or not. If it is equal it returns a true value otherwise false
2. In a++,++is a post(means after the operand) increment operator and in ++a, ++ is a pre(means before the operand) increment operator. They are entirely different.
Post increment:
Here first use the value of ‘a’ and then change the value of ‘a’.
Eg: if a= 10 then b=a++. After this statement b= 10 and a=11
Pre increment:
Here first change the value of a and then use the value of a.
Eg: if a=10 then b=++a. Afterthis statement b=11 and a=11.

Question 18.
Consider the following
int a=45.65;
cout<<a;
What is the output of the above. Is it possible to convert a data type to another type? Explain.
Answer:
The output of the code is 45, the floating-point number is converted into integer. It is possible to convert a data type into another data type. Type conversions are two types.
1. Implicit type conversion:
This is performed by C++ compiler internally. C++ converts all the lower sized data type to the highest sized operand. It is known as type promotion. Data types are arranged lower size to higher size is as follows, unsigned int(2 bytes), int(4 bytes), long(4 bytes), unsigned long(4 bytes), float(4 bytes), double(8 bytes), long double(10 bytes).
2. Explicit type conversion:
It is known as type casting. This is done by the programmer. The syntax is given below.
(data type to be converted) expression
Eg.int x=10;
(float) x; This expression converts the data type of the variable from integer to float.
Question 19.
Your friend Arun asked you that is there any loop that will do three things, initialization, testing, and updation. What is your answer? Explain?
Answer:
Yes. There is only one loop namely for loop that will do this three things. The other loops will do the checking only, initialisation must be do before the loop and updation must be inside the loop.
The syntax of for loop is given below
For(initialisation; testing; updation)
{
Body of the for loop;
}
Question 20.
Distinguish between exit(0) function and return statement
Answer:
Both are used to terminate the program but both are different. Return is a keyword and exit(O) is a function. The difference is, we can use more than one exit(0) function but we can use only one return statement in a scope. To use exit(0), the header file cstdlib should be used.

Question 21.
Rewrite the program following program using if else
#include
using namespace std;
int main()

Answer:
# include
using namespace std;
int main()

Question 22.
Rewrite the following using nested switch construct.
#include
using namespace std;
int main()


Answer:
#include
using namespace std;
int main()


Question 23.
Consider the following output and write down the code for the same.

Answer:
include
using namespace std;
int main()

Question 24.
Consider the following output and write down the code for the same.

Answer:
# include
using namespace std;
int main()

Question 25.
Consider the following output and write down the code for the same.
Answer:
# include
using namespace std;
int main()


Question 26.
Consider the following output and write down the code for the same.
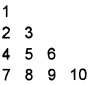
Answer:
# include
using namespace std;
int main()

Question 27.
Consider the following output and write down the code for the same.

Answer:
#include
using namespace std;
int main()

Question 28.
Consider the following output and write dawn the code for the same.

Answer:
#include
using namespace std;
int main()


Question 29.
Write a program to print the sum of first n natural numbers
Answer:
# include
using namespace std;
int main()
int n,i,sum=0;
cout<<“Entera value torn”; cin>>n;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)

Question 30.
Write a program to read a number and check whether it is palindrome or not
Answer:
# include
using namespace std;
int main()

Question 31.
Write a program to print the factorial of a number.
Answer:
#include
using namespace std;
int main()


Question 32.
Write a program to print the Fibonacci series Fibonacci
Answer:
# include
using namespace std;
int main()


Question 33.
Write a program to read a number and check whether the given number is Armstrong or not
Answer:
# include
using namespace std;
int main()

Question 34.
Distinguish between entry controlled loop and exit controlled loop
Answer:
An entry controlled loop first checks the condition and execute(or enters in to) the body of loop only if it is true. But exit control loop first execute the body of the loop once even if the condition is false then check the condition. The for loop and while loop are entry controlled loops but do-while loop is an exit controtted loop.

Question 35.
Write a program to find the largest of 3 numbers
Answer:
#include
using namespace std;
int main()

Question 36.
Check whether a given number is prime or not
Answer:
#include
using namespace std;
int main()

Question 37.
Write a program to read number and display its factors.
Answer:
# include
using namespace std;
int main()


Question 38.
You are given the heights of 3 students. Write the relevant code segment to find the maximum height?
Answer:
# include
using namespace std;
int main()

Question 39.
Write the easiest code snippet for printing your name 1000 times. Explain
Answer:
# include
using namespace std;
int main()

Question 40.
Whenever a string is entered the inverse of that string is displayed( eg: if we enter ‘CAR’ the output is ‘RAC’). Write a suitable programme for the output.
Answer:
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()


Question 41.
Write a C++ program to display as follows
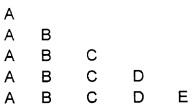
Answer:
#include
using namespace std;
int main()

OR
#include
using namespace std;
int main()

Question 42.
Consider the following code The new line.character is \n. The output of the following code does not contain the \n. Why it is happened? Explain.
Answer:
\n is a character constant and it is also known as escape sequence. This is used to represent the non graphic symbols such as carriage return key(enter key), tab key, back space, space bar, etc. It con¬sists of a back slash symbol and one more characters.
| Escape sequence |
Non-graphic character |
| \a |
Audible bell |
| \b |
back space |
| \n |
for new line |
| \r |
carnage return |
| \t |
horizontal tab |
| \v |
vertical tab |
| \\ |
to print \ |
| \’ |
to print ‘ |
| \” |
to print ” |
| \? |
To print? |
| \0 |
null character |

Question 43.
The Maths teacher gives the following problem to Riya and Raju.
x= 5 + 3 * 6. Riya got x = 48 and Raju got x = 23. Who is right and why it is happened? Write down the operator precedence in detail?
Answer:
Here the answer is x = 23. It is because of precedence of operators. The order of precedence of operators are given below.
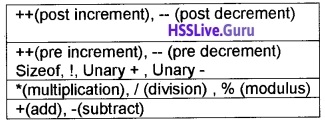
Here multiplication has more priority than addition.
Question 44.
Rewrite the following code using while and do..while loop.
for(i=1;i<5;++i)
{
cout<<“\n”<<i;
}
Answer:
1. using while loop
i=1;
while(i<=5)
{
cout<<“\n”<<i;
i++;
}
2. using do while loop
i=1;
do
cout<<“\n”<<i;
i++;
}while(i<=5);

Question 45.
Rewrite the following C++ code using switch
statement.

Answer:
switch(choice)

Question 46.
Considerthe following code and predict the output
int a=5, b=6, c=7;
if (a<b) || b>c)
cout<<“\nOne”;
if (a<b&&b>c)
cout<<“\nTwo”; if (! *a>b)
cout<<“\nThree”;
Answer:
case 1:
if(ac)
cout<<“\nOne”;
here ac
5<6 || 6>7
True || False = True.
This condition returns True
Hence it prints One.
case 2:
if(ac)
cout<<“\nTwo”;
here ac
5<6 && 6>7
True && False = False
This condition returns False
Hence it prints nothing.
Case 3:
if(! (a>b))
cout<<“\nThree”); here !(a>b)
! (5 >6)
! (False)
This condition returns True
Hence it prints Three.

Question 47.
Match the following
| Name |
Symbol |
| Modulus operator |
+ + |
| Logical operator |
= = |
| Relational operator |
= |
| Assignment operator |
?= |
| Increment operator |
% |
| Conditional operator |
&& |
Answer:
| Name |
Symbol |
| Modulus operator |
% |
| Logical operator |
&& |
| Relational operator |
= = |
| Assignment operator |
= |
| Increment operator |
+ + |
| Conditional operator |
?= |
Question 48.
Write a C++ program to calculate the simple interest SI, by accepting the value principal amount P, rate of interest R and number of years N using the equation SI = PNR/100.
Answer:
# include
using namespace std;
int main()


Question 49.
Rewrite the following conditional statement with ‘if statement in C++.
min=(a<b) ? (a<c? a:c) : (b<c? b:c);
Answer:
if(a<b && a<c)
min=a;
else if(b<c) min=b; else min=c;
Plus Two Computer Application Review of C++ Programming Five Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Define operator and explain operators in detail. Operators
Answer:
An operator is a symbol that performs an operation. The data on which operations are carried out are called operands. Following are the operators.
1. Input(>>) and output(<<) operators are used to perform input and output operation. Eg. cin>>n; cout<<n;
2. Arithmetic operators:
It is a binary operator. It is used to perform addition(+), subtraction (-), division (/), multiplication (*) and modulus (%-gives the remainder) operations.
Eg. If x=10 and y=3 then

x/y = 3, because both operands are integer. To get the floating point result one of the operand must be float.
3. Relational operator:
It is also a binary operator. It is used to perform comparison or relational operation between two values and it gives either true(1) or false(O). The operators are <,<=,>,>=,== (equality)and !=(not equal to)
Eg. If x=10 and y=3 then

4. Logical operators:
Here AND(&&), OR (||) are binary operators and NOT (!) is a unary operator. It is used to combine relational operations and it gives either true (1) or false (0).
If x=1 and y=0 then
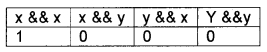
Both operands must be true to get a true value in the case of AND (&&) operation
If x=1 and y=0 then

Either one of the operands must be true to get a true value in the case of OR(||) operation
If x=1 and y=0 then

5. Conditional operator:
It is a ternary operator hence it needs three operands. The operator is?: Syntax: expression? value if true: value if false. First evaluates the expression if it is true the second part will be executed otherwise the third part will be executed.
Eg. If x=10 and y=3 then
x>y? cout<< Here the output is 10.
6. sizeof():
This operator is used to find the size used by each data type.
Eg. sizeof(int) gives 2.
7. Increment and decrement operator:
These are unary operators.
- Increment operator (++): It is used to increment the value of a variable by one i.e., x++ is equivalent to x=x+1;
- Decrement operator (–): It is used to decrement the value of a variable by one i.e., x- is equivalent to x = x-1.
8. Assignment operator (=):
It is used to assign the value of a right side to the left side variable.eg. x=5; Here the value 5 is assigned to the variable x.

Question 2.
A list of data items are given below
45, 8.432, M, 0.124, 8, 0, 8.1X 1031, 1010, a, 0.00025, 9.2 × 10120, 0471, -846, 342.123E03
- Categorise the given data under proper headings of fundamental data types in C++
- Explain the specific features of each data type. Also mention any other fundamental data type for which sample data is not given
Answer:
1.

2.
(i) int data type:
It is used to store whole numbers without fractional (decimal point) part. It can be either negative or positive. It consumes 4 bytes (32 bits) of memory. i.e. 232 numbers. That is 231 negative numbers and 231 positive numbers (0 is considered as +ve) So a total of 232 numbers. We can store a number in between -231 to + 231-1.
(ii) char data type:
Any symbol from the key board, eg. ‘A’,’?’, ‘9’,___It consumes one byte( 8 bits) of memory. It is internally treated as integers, i.e. 28 = 256 characters. Each character is having a ASCII code, ‘a’ is having ASCI I code 97 and zero is having ASCII code 48.
(iii) float data type:
It is used to store real numbers i.e. the numbers with decimal point. It uses 4 bytes(32 bits) of memory. Eg. 67.89, 89.9 E-15.
(iv) double data type:
It is used to store very large real numbers. It uses 8 bytes(64 bits) of memory.
void data type:- void means nothing. It is used to represent a function returns nothing.
Question 3.
Write valid reasons after reading the following statements in C++ and comment on their correctness by give reasons.
- char num = 66;
- char num – B’;
- 35 and 35L are different
- The number 14,016 and OxE are one and the same
- Char data type is often said to be an integer type
- To store the value 4.15 float data type is preferred over double
Answer:
- The ASCII number of B is 66. So it is equivalent.
- 35 is of integer type but 35L is Long
- The decimal number 14 is represented in octal is 016 and in hexadecimal is OxE.
- Internally char data type stores ASCII numbers.
- To store the value 4.15 float data type is better because float requires only 4 bytes while double needs 8 bytes hence we can save the memory.

Question 4.
Suggest most suitable derived data types in C++ for storing the following data items or statements
- 0 Age of 50 students in a class
- Address of a memory variable
- A set of instructions to find out the factorial of a number
- An alternate name of a previously defined variable
- Price of 100 products in a consumer store
- Name of a student
Answer:
- Integer array of size 50
- Pointer variable
- Function
- Reference
- Float array of size 100
- Character array
Question 5.
Considering the following C++ statements. Fill up the blanks
- lf p=5 and q=3 then q%p is _____
- If E1 is true and E2 is False then E1 && E2 will be_____
- If k=8, ++k <= 8 will be______
- If x=2 then (10* ++x) % 7 will be_____
- If t=8 and m=(n=3,t-n), the value of m will be______
- If i=12 the value i after execution of the expres¬sion i+=i– + –i will be______
Answer:
- 3
- False
- False(++k makes k=9. So 9<=8 is false)
- 2(++x becomes 3, so 10 * 3 =30%7 =2)
- 5( here m=(n=3,8-3)=(n=3,5), so m=5, The maximum value will take)
- Here i=12
i + = i– + –i
here post decrement has more priority than pre decrement. So i — will be evaluated first. Here first uses the value then change so it uses the value 12 and i becomes 11
i + =12 + –i
now i =11.
Here the value of i will be changed and used so i– becomes 10
i + = 12 + 10
= 22
So i = 22 + 10
i = 32
So the result is 32.

Question 6.
Analyses the following statements and write Time or False. Justify
- There is an Operator in C++ having no special character in it
- An operator cannot have more than 2 operands
- Comma operator has the lowest precedence
- All logical operators are binary in nature
- It is not possible to assign the constant 5 to 10 different variables using a single C++ expression
- In type promotion the operands with lower data type will be converted to the highest data type in expression
Answer:
- True (sizeof operator)
- False( conditional operator can have 3 operands
- True
- False
- False(Multiple assignment is possible, eg: a=b=c=___=5)
- True
Question 7.
Match the following numbers and data types in C++ to form the most suitable pairs.
| 1. 142789 |
a. Signed |
| 2. 240 |
b. Double |
| 3. -150 |
c. Long int |
| 4. 8.4 × 10-4000 |
d. Float |
| 5. 0 |
e. Long double |
| 6. 0.0008 |
f. Unsigned short |
| 7. -127 |
g. Short int |
| 8. 2.8 × 10308 |
h. Signed char |
Answer:
| 1. 142789 |
a. Long int |
| 2. 240 |
b. Short int |
| 3. -150 |
c. Signed |
| 4. 8.4 × 10-4000 |
d. Long double |
| 5. 0 |
e. Unsigned short |
| 6. 0.0008 |
f. Float |
| 7. -127 |
g. Signed char |
| 8. 2.8 × 10308 |
h. Double |

Question 8.
#include
using namespace std;
int main()

Rewrite the above code using if else if ladder.
Answer:
#include
using namespace std;
int main()


Question 9.
Consider the following code
# include
using namespace std;
int main()

Is it possible to rewrite the above program using switch statement? Distinguish between switch and if else if ladder. Answer:
No. It is not possible to write the above code using switch statement. Following are the difference between switch and if else if ladder.
- Switch can test only for equality but if can evaluate a relational or logical expression
- If else is more versatile
- If else can handle floating values but switch can not
- If the test expression contains more variable if else is used
- Testing a value against a set of constants switch is more efficient than if else

Question 10.
Write down the code for the following output using while loop.

Answer:
# include
using namespace std;
int main()

Question 11.
“We know that the execution of a program is sequential”. Is it possible to change this sequential manner and explain different jump statements in detail.
Answer:
The execution of a program is sequential but we can change this sequential manner by using jump statements. The jump statements are
1. goto statement:
By using goto we can transfer the control anywhere in the program without any condition. The syntax is goto label; Eg. # include
using namespace std;
int main()

2. break statement:
It is used to skip over a part of the code i.e. we can premature exit from a loop such as while, do-while, for or switch. Syntax:
while (expression)

The output is
1
2
3
4
5.
3. continue statement:
It bypasses one iteration of the loop.
Syntax:
while (expression)

The output is
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10.
4. exit(O) function:
It is used to terminate the program. For this the header file cstdlib must be included.

Question 12.
Write a program to print the prime numbers less than 100
Answer:
# include
using namespace std;
int main()

Question 13.
Write a program to print the Armstrong numbers less than 1000
Answer:
# include
using namespace std;
int main()

Question 14.
Given the total mark of each student in SSLC examination. Write a C++ code fragment to find the grades.
Answer:
# include
using namespace std;
int main()


Question 15.
You are about to study the fundamentals of C++ programming Language. Do a comparative study of the basics of the new language with that of a formal language like English or Malayalam to familiarize C++?. Provide sufficient explanations for the compared items in C++ Language.
Answer:
Character set:
To study a language first we have to familiarize the character set. For example to study English language first we have to study the alphabets. Similarly here the characterset includes letters(A to Z & a to z), digits(0 to 9), special characters(+,-,?,*,/,___) white spaces(non printable) etc. Token: It is the smallest individual units similar to a word in English or Malayalam language. C++ has 5 tokens
1. Keywords:
These are reserved words for the compiler. We can’t use for any other purposes
Eg: float is used to declare variable to store numbers with decimal point. We can’t use this for any other purpose
2. Identifier:
These are user defined words.
Eg: variable name, function name, class name, object name etc….
3. Literals (Constants):
Its value does not change during execution
Eg: In maths pi = 3.14157 and boiling point of water is 100.
4. Punctuators:
In English or Malayalam language punctuation mark are used to increase the read ability but here it is used to separate the tokens.
Eg:{.}.(.)…..
5. Operators:
These are symbols used to perform an operation(Arithmetic, relational, logical,etc…)code, the middle button displays the object and the right button toggles the folder.

Question 16.

Consider the above data, we know that there are different types of data are used in the computer. Explain different data types used in C++.
Answer:
1. int data type:
It is used to store whole numbers without fractional (decimal point) part. It can be either negative or positive. It consumes 2 bytes(16 bits) of memory.i.e. 216 = 65536 numbers. We can store a number in between -32768 to + 32767.
2. char data type:
Any symbol from the keyboard, eg. ‘A’,’9′,…. It consumes one byte( 8 bits) of memory. It is internally treated as integers, i.e. 28 = 256 characters. Each character is having a ASCII code, ‘a’ is having ASCII code 97 and zero is having ASCII code 48.
3. float data type:
It is used to store real numbers i.e. the numbers with decimal point. It uses 4 bytes(32 bits) of memory. Eg. 67.89, 89.9 E-15.
4. double data type:
It is used to store very large real numbers. It uses 8 bytes(64 bits) of memory.
5. void data type:
void means nothing. It is used to represent a function returns nothing.

Question 17.
Explain conditional statements in detail?
Answer:
1. Simple if:
The syntax is given below
if(expression)
statement;
or
if(expression)
{
Block of statements
}
First expression evaluates if it is true then only statement will be executed.
Eg. if (n>0)
cout<<n<<” is positive”;
2. if else:
The syntax is given below.
if (expression)

First expression evaluates if it is true statement block 1 will be executed otherwise statement block 2 will be executed. Only one block will be executed at a time so it is called branching statement.
Eg.
if (n>0)
cout<<n<<” is positive”;
else
cout<<n<<” is negative”;
3. if else if ladder:
The syntax will be given below
if (expression 1)

Here first expression 1 will be evaluated if it is true only the statement block 1 will be executed otherwise expression 2 will be executed if it is true only the statement block2 will be executed and soon. If all the expression evaluated is false then only statement block n will be evaluated.
Eg.
If(mark>=90)
cout«<<“Your grade is A+”;

4. conditional operator:
It is a ternary operator and it is an alternative for if else construct. The syntax is given below. expression 1? expression 2: expression 3; or expression 1? Value if true: value if false; Here expression 1 will be evaluated if it true ex¬pression 2 will be executed otherwise expression 3 will be executed. Eg. n>0?cout<<n<<” is positive”:cout<<n<<” is negative”;
5. Switch:
It is a multiple branch statement. Its syntax is given below.
switch(expression)



Question 18.
Explain different loops in detail?
Answer:
1. For loop:
The syntax of for loop is
for(initialization; checking ; update loop variable)
{
Body of loop;
}
First part, initialization is executed once, then checking is carried out if it is true the body of the for loop is executed. Then loop variable is updated and again checking is carried out this process continues until the checking becomes false. It is an entry controlled loop.
Eg. for(i=1 ,j=1 ;i<=10;i++,j++)
cout<<i<<” * “<<j<<” = “<<i*j;
2. While loop:
It is also an entry controlled loop
The syntax is given below
Loop variable initialised
while(expression)
{
Body of the loop;
Update loop variable;
}
Here the loop variable must be initialised out side the while loop. Then the expression is evaluated if it is true then only the body of the loop will be executed and the loop variable must be updated inside the body. The body of the loop will be executed until the expression becomes false.
Eg.
i=1;
j=1;
while(i<=10)
{
cout<<i<<” * “<<j<<” = “<<i*j;
i++;
j++;
}
3. do While loop:
It is an exit controlled loop.
The syntax is given below
do
{
Statements
}while(expression);
Here the body executes atleast once even if the condition is false. After executing the body it checks the expression if it false it quits the body otherwise the process will be continue.

Question 19.
Write a program to find simple interest and compound interest.
Answer:
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;

Question 20.
Mr. X wants to get an output 9 when inputting 342 and he also wants to get 12 when inputting 651. Write the program and draw a suitable flowchart for X?
Answer:
Flow chart
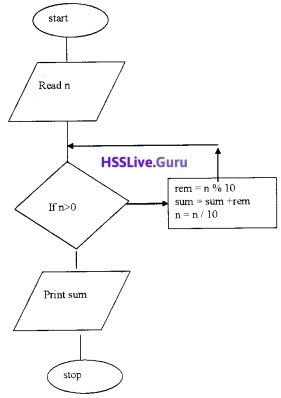
#include
using namespace std;
int main()


Question 21.
Differentiate break and continue statements with suitable examples.
Answer:
1. break statement:
It is used to skip over a part of the code i.e. we can premature exit from a loop such as while, do-while, for or switch.
Syntax:
while (expression)

The output is
1
2
3
4
5.
2. continue statement:
It bypasses one iteration of the loop.
Syntax :
while (expression)

The output is
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10.

Question 22.
Write a C++ program to print to get the following output.

Answer:
#include
using namespace std;
int main()